Coating carbide inserts is an integral element in enhancing the effectiveness, performance, and durability of these cutting tools.
When you buy coated carbide inserts, you can be certain of a tool with improved wear-resistance and enabled high speeds and feeds.
However, using the right type of coating is what guarantees you desirable results.
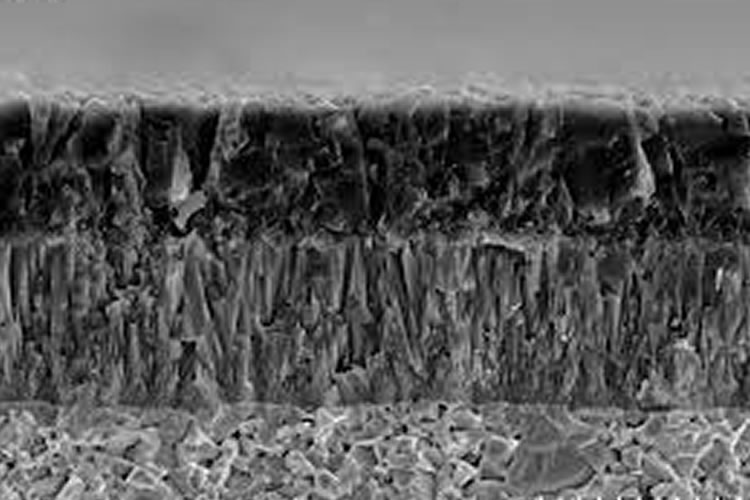
There are two main methods utilized for coating, which include Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
CVD coating is based on chemical reactions in a relatively vaporized medium.
On the other hand, PVD utilizes material spluttering.
The PVD process is a comparatively low-temperature process offering a finer crack-resistant grain structure with a low coefficient of friction.
Consequently, PVD-coated carbide inserts can have sharper cutting edges.
The deposition processing temperature distinguishes PVD and CVD coatings.
Technology development enables both CVD and PVD to be combined for coating cemented carbides to regulate coating properties.
Characteristically, CVD coating types have excellent build-up edge resistance and effective at lower speeds.
Also, they are excellent on gummy materials and for threading and cut-off operations. Moreover, this coating type makes it easy to identify the specific carbide insert corners that have been used.
PVD coating types, on the other hand, are effective in high-temperature alloys, stainless steel, and end mills.
You can use it on a broad range of applications, including turning, milling, and drilling among others.